Prostatitis
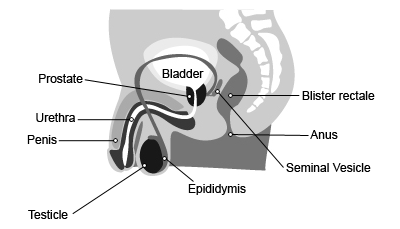
The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that is around the size of a walnut. It secretes certain components of sperm. The gland is located under the bladder in front of the rectum and surrounds the urethra.
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate and causes the prostate to become enlarged. As the prostate grows, it compresses the urethra and reduces the space available for urine to pass through.
Symptoms vary according to the type of prostatitis. Pain and genitourinary problems (e.g., difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, erectile dysfunction) may occur.
Causes and triggers
There are 4 types of prostatitis:
| Type of prostatitis | Cause and frequency | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Acute bacterial prostatitis | Caused by bacteria. Uncommon. | Painful symptoms arise suddenly and intensely. Examples: difficulty urinating, fever, chills, general malaise. |
| Chronic bacterial prostatitis (long-term) | Caused by bacteria. Uncommon. | Symptoms are less intense than the acute form. Can last months. Often not accompanied by a fever. |
| Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis (chronic pelvic pain syndrome) | Not caused by bacteria. This is the most common type. | Pain or discomfort is felt in the pelvis. Symptoms may come and go. |
| Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis | The cause remains uncertain. | No symptoms. Typically diagnosed when screening for other diseases. |
When prostatitis is caused by a sexually transmitted infection, the infection may be contagious.
The following factors may increase the risk of developing prostatitis:
- Bladder spasms or spasms of the muscles surrounding the bladder
- Obstruction of the bladder or ejaculatory duct
- Trauma to the pelvis
- Recent bladder or urinary tract infection
- Recent insertion of a urinary catheter
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis. When prostatitis is bacterial in nature, an antibiotic may be prescribed. Additional medications may be prescribed as a complementary treatment to relieve symptoms.
Other measures may also help reduce associated symptoms, including the following:
- Sitz baths
- Applying heat locally
- Physical therapy (e.g., Kegel exercises, prostate massage, relaxation)
- Increasing fluid intake
- Surgery
At this time, no proven prevention strategy has been shown to ward off prostatitis.
When should I see a health care professional?
Speak with your health care provider in the following situations:
- You have difficulty starting or stopping urination
- You notice that the strength of your urine stream or the amount of urine you pass is decreasing
- You still have the urge to urinate after emptying your bladder
- You have the urge to urinate more frequently
- You feel an urgent need to urinate
- You feel pain or a burning sensation when you urinate
- You experience sexual or erectile dysfunction
- You notice blood in your urine or semen
- You have persistent back, hip, and pelvic pain
For more information:
[UNIPRIX] © Copyright Vigilance Santé
The patient information leaflets are provided by Vigilance Santé Inc. This content is for information purposes only and does not in any manner whatsoever replace the opinion or advice of your health care professional. Always consult a health care professional before making a decision about your medication or treatment.
